
Role of Genetics and RNA in Neurologic Diseases
Role of Genetics and RNA in Neurologic Diseases
Many neurologic diseases have a genetic component.1-5
Neurologic diseases can be caused by genetic variants that alter protein structure and/or production. Over 1700 distinct genetic variants have been identified as contributing to a range of neurodegenerative, neuromuscular, and neurodevelopmental diseases.1-5
The 4 most common types of genetic variants are point mutations, copy number variants, small insertions and deletions (InDels), and chromosomal rearrangements.6
Types of Genetic Variants6
Point mutations
Copy number variants
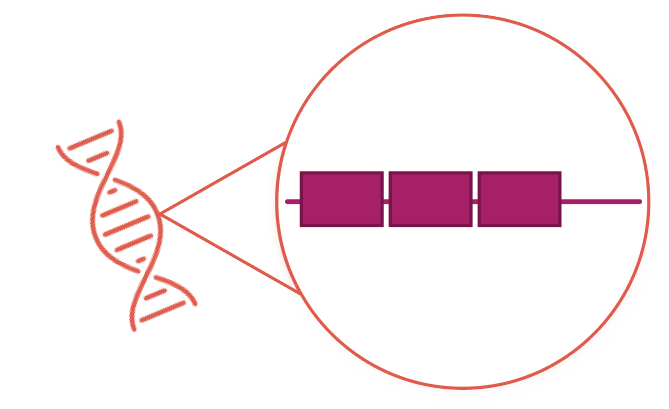
Small InDels

Chromosomal rearrangements


Examples:
For example, in Alexander disease (AxD), point mutations or InDels in the glial fibrillary acidic protein gene (GFAP) can alter protein accumulation.7 In Angelman syndrome (AS), the majority of cases (~70%-75%) are caused by deletions in the UBE3A gene, leading to the most severe symptoms.8-12
Unmet Needs:
Despite advancements in understanding the pathology of neurologic diseases, many of these genetic targets are not readily treatable by traditional small molecules or antibody therapeutics.13
RNA has emerged as a unique target for developing therapeutics because of the broad applicability, translational utility, and efficiency of the drug discovery processes.14,15
References
- Schüle R, Timmann D, Erasmus CE, et al. Solving unsolved rare neurological diseases—a Solve-RD viewpoint. Eur J Hum Genet. 2021;29(9):1332-1336.
- Bennett CF, Kordasiewicz HB, Cleveland DW. Antisense drugs make sense for neurological diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021;61:831-852.
- de Rojas I, Moreno-Grau S, Tesi N, et al. Common variants in Alzheimer’s disease and risk stratification by polygenic risk scores [published correction appears in Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 9;14(1):716]. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3417.
- Maranga C, Fernandes TG, Bekman E, da Rocha ST. Angelman syndrome: a journey through the brain. FEBS J. 2020;287(11):2154-2175.
- Picher-Martel V, Brunet F, Dupré N, Chrestian N. The occurrence of FUS mutations in pediatric amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a case report and review of the literature. J Child Neurol. 2020;35(8):556-562.
- Ku CS, Loy EY, Salim A, Pawitan Y, Chia KS. The discovery of human genetic variations and their use as disease markers: past, present and future. J Hum Genet. 2010;55(7):403-415.
- Messing A. Alexander disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;148:693-700.
- Wheeler AC, Sacco P, Cabo R. Unmet clinical needs and burden in Angelman syndrome: a review of the literature. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12(1):164.
- Larson AM, Shinnick JE, Shaaya EA, Thiele EA, Thibert RL. Angelman syndrome in adulthood. Am J Med Genet A. 2015;167A(2):331-344.
- Prasad A, Grocott O, Parkin K, Larson A, Thibert RL. Angelman syndrome in adolescence and adulthood: a retrospective chart review of 53 cases. Am J Med Genet A. 2018;176(6):1327-1334.
- Mertz LG, Christensen R, Vogel I, et al. Angelman syndrome in Denmark. Birth incidence, genetic findings, and age at diagnosis. Am J Med Genet A. 2013;161A(9):2197-2203.
- Hagenaar DA, Bindels-de Heus KGCB, Lubbers K, et al. Child characteristics associated with child quality of life and parenting stress in Angelman syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2024;68(3):248-263.
- Bennett CF, Krainer AR, Cleveland DW. Antisense oligonucleotide therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2019;42:385-406.
- Crooke ST, Liang XH, Baker BF, Crooke RM. Antisense technology: a review. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100416.
- Ionis Pharmaceuticals. The creation of RNA targeting technology. December 2019. Accessed July 15, 2025. https://ir.ionispharma.com/static-files/1cada39c-0fa4-4e90-afdf-e85fa258e03b/
